Synchronous motor always runs at synchronous speed. That’s why it is known as synchronous motor. It is kind of AC electrical machine that is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
this is one of the important topic from electrical machine so in this article we will learn construction and working principle of synchronous motor
Construction of synchronous motor
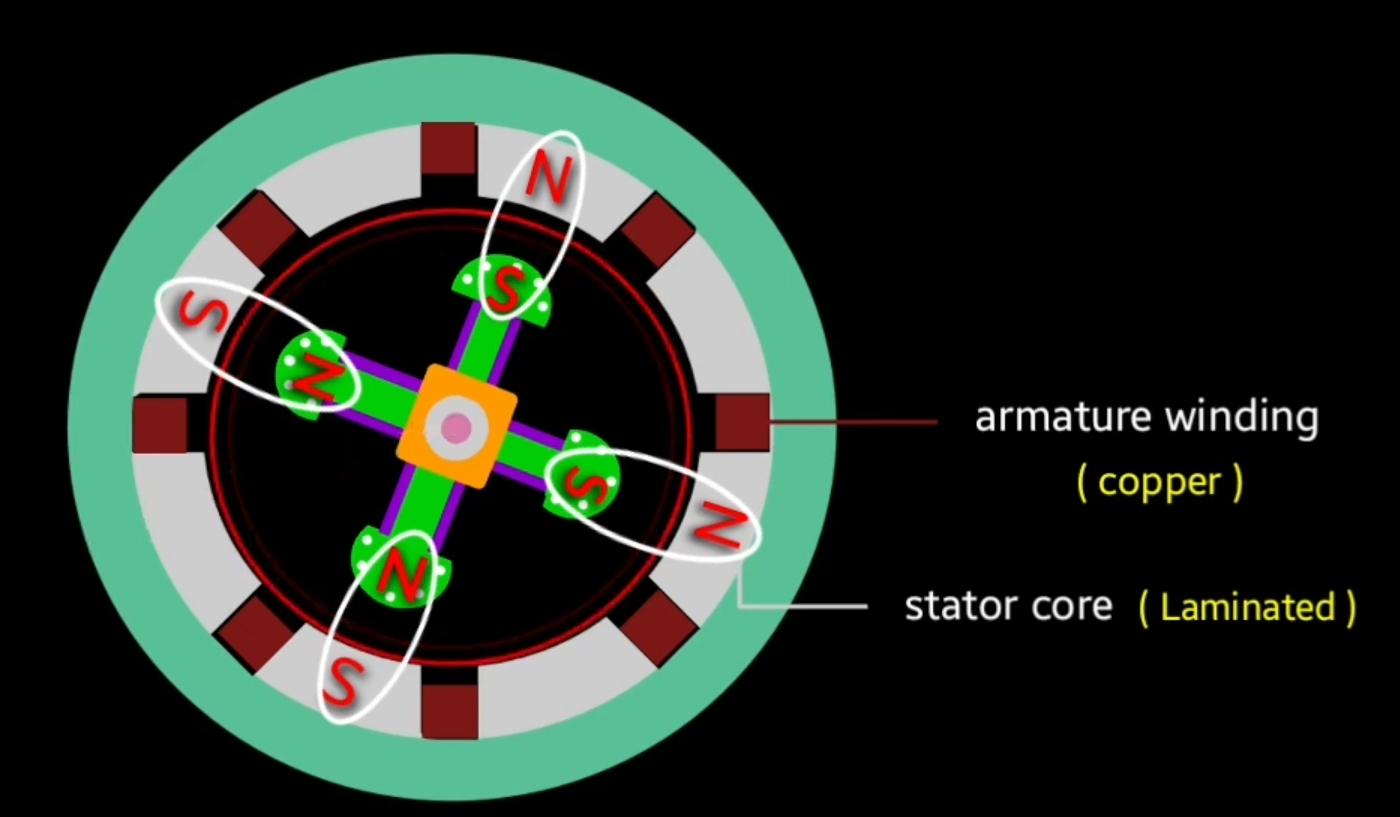
Synchronous motor consists with two main part that is stator and rotor.
in case of synchronous machine field winding is placed on rotor and armature winding is placed on the stator this is key point of synchronous machine.
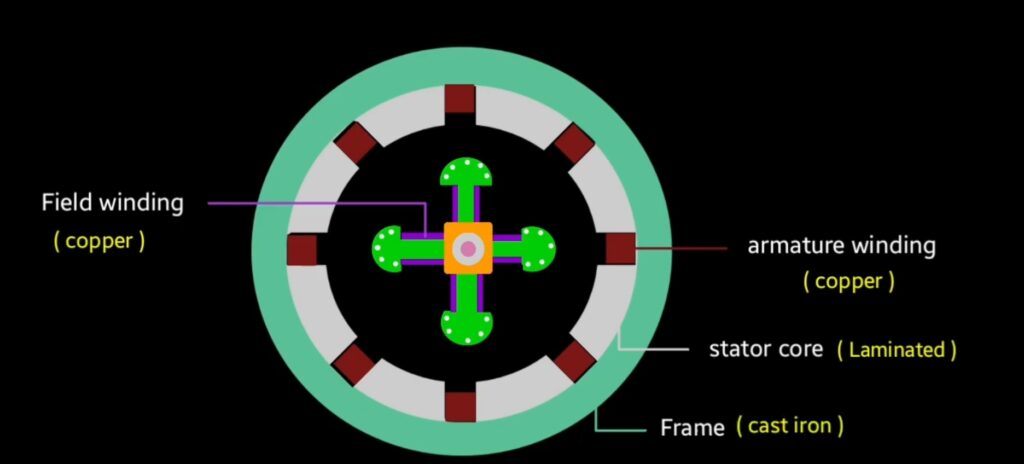
Stator : stator is the stationary part of synchronous machine . Status core is made up of silicon Steel that offer high permeability property and low reluctance path for the magnetic field lines. At the inner portion of a stator slots are present where we place three phase copper winding. And that winding is known as three phase armature winding.
we provide lamination on stator Core to reduce the Eddy current loss, lamination is the arrangement of various thin strips that joins together to make core of machine we provide lamination to reduce electrical losses.
Salient pole rotor : in synchronous machine we can use two types of rotor salient pole rotor and non salient pole rotor , in this article we have consider salient pole rotor to explain it’s working.
the pole of rotor are projected towards armature winding that’s why it is known as salient Pole rotor, field winding is placed on the pole of salient pole rotor. Generally we use copper material for winding due to their good electrical conductivity so armature winding and field winding both are made up of copper material.
Frame : outer body of synchronous machine is known as frame that is made up of cast iron. It protect the internal assembly of the motor from any type of damage.
Synchronous motor working principle
first we give three phase AC supply in stator winding of synchronous motor

When three phase AC supply given to the stator winding (armature winding) then due to three phase winding that placed on 120 degree electrical , rotating magnetic field produces in the air gap of rotor and stator that rotates at synchronous speed that is given by
(Ns = 120 F/P )
- F – frequency
- P – pole
- Ns – synchronous speed
as we know frequency is present in AC current so field polarity of rotating magnetic field changes with respect to frequency. If the frequency of supply voltage is 50 hz then polarity will changes respectively.
as well as we give DC excitation in field winding which place on the rotor pole. As we know DC supply is frequency less so if we are providing DC current on field winding that placed on rotor then constant magnetic field produces that will not change with respect to time.
in case of synchronous motor we give supply at both place stator as well as rotor that’s why this type of machine is also known as doubly excited motor
synchronous motor is not a self start motor, to start the motor we use external prime mover that reaches the speed of rotor at synchronous speed . As a prime mover small induction motor or DC motor is used , shaft of prime mover is coupled with synchronous motor shaft and we rotate the rotor of synchronous motor at synchronous speed.
When speed of rotor reaches to the speed equal to rotating magnetic field , opposite polarity of magnetic poles get interlock , n-pole and s-pole interlocked to each other . After interlocking external prime mover removed from shaft of synchronous motor.

and rotor of synchronous motor rotates continuously with rotating magnetic field at synchronous speed. Thus synchronous motor continue rotates at synchronous speed.
Important points
- this motor does not depends on load mean if we vary the load then speed of the motor will not change
- synchronous motor is not a self starting motor it has requirement of external prime mover to start the motors.