Repulsion motor is the special purpose machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy where mechanical output can be torque or force. Repulsion Motor is the single phase induction motor that operates on AC supply its main application is in trains and higher starting torque applications. This type of motor Operates on the principle of magnetic repulsion.
Construction of repulsion motor
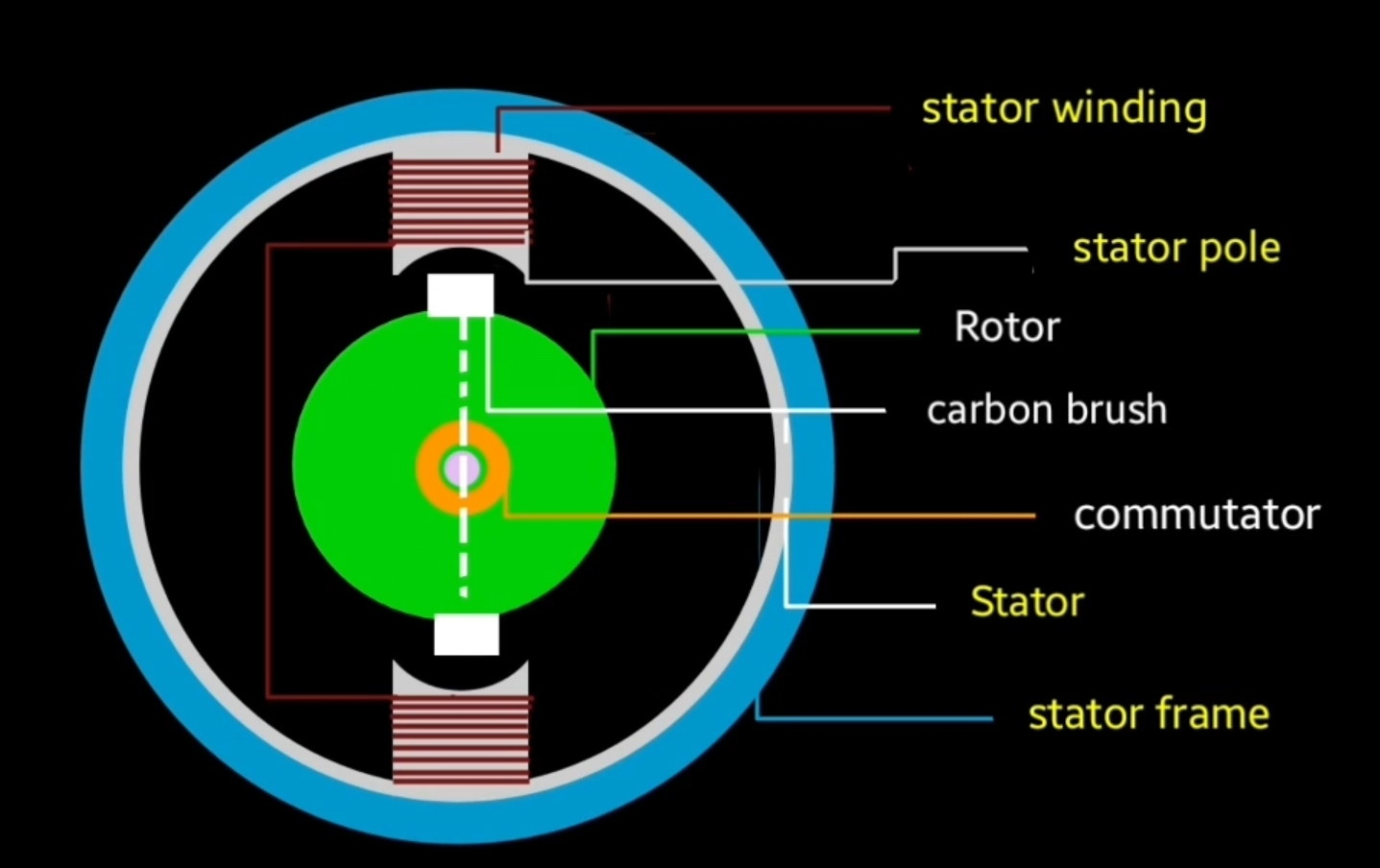
Repulsion motor consist with different main parts like other type of electric motors.
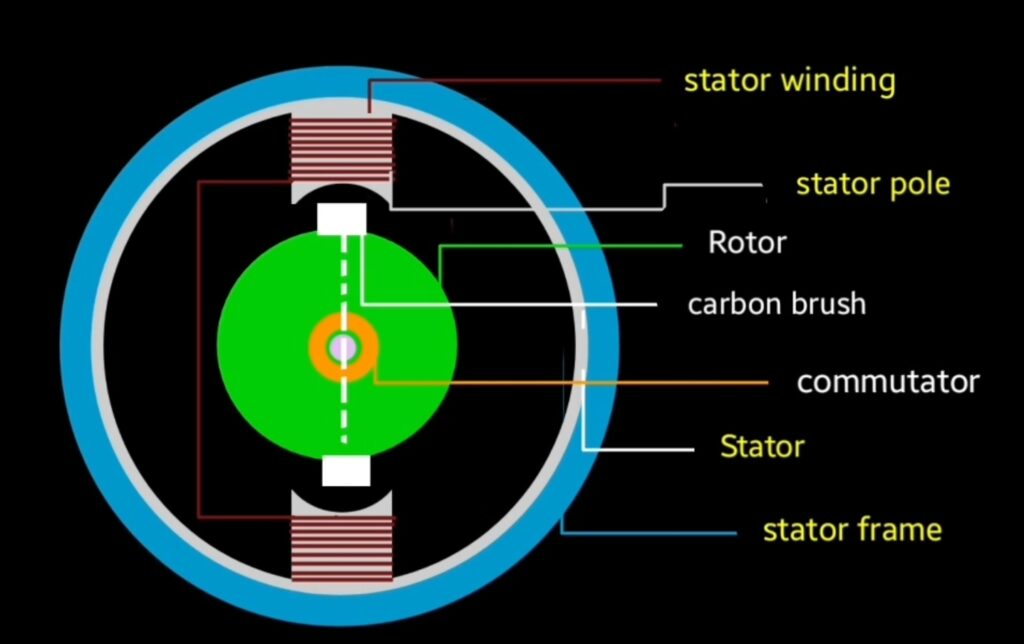
It’s construction is almost as single phase induction motor. It have also to important part stator and rotor
Stator : stator is the stationery part of motor that remain fixed at one place. Poles are present at the inner portion of stator core where stator winding is placed that is made up of copper due to their good electrical conductivity.
Rotor : rotor is the rotating part of repulsion motor , carbon brushes and commutator is attached with the rotor it’s rotor construction is almost similar like other motors. Main difference is here in repulsion motor rotor brushes are short circuited.
Working principle of repulsion motor
when we give single phase AC supply to the stator winding then due to inductive winding around the stator pole variable magnetic flux produces. Field polarity will varies or changes due to frequency in AC supply.
suppose during positive cycle of AC supply N-pole develops on top pole and S-pole develops on bottom pole. In case of repulsion motor direction of torque on rotor will determine by the position of rotor brushes. So to understand the working of repulsion motor we consider three cases where we will change the position of rotor brushes, will analyse the direction of torque on rotor.
Case – 1 : when brush axis is aligned with field axis.

as you can see in the above diagram here angle between the brush axis and field axis is (0°) . Since changing magnetic field is produces around the top and bottom stator due to single phase AC supply and that changing magnetic field cuts the rotor conductors so due to relative motion between changing magnetic flux and stationery rotor conductor , EMF induces in the conductor from ” Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction “
since rotor brushes are short circuited and due to EMF induced in the conductor current will circulate in the rotor winding and due to that current magnetic polarity will develop on the rotor conductors like ( N-pole & S-pole )
in this condition upper half conductors of rotor experiences the force in downward direction and lower half conductor experience the force in upward direction. That’s why net torque becomes zero and at this position of brush rotor does not rotate in any direction.
Case – 2 : When brush axis is perpendicular to the field axis.
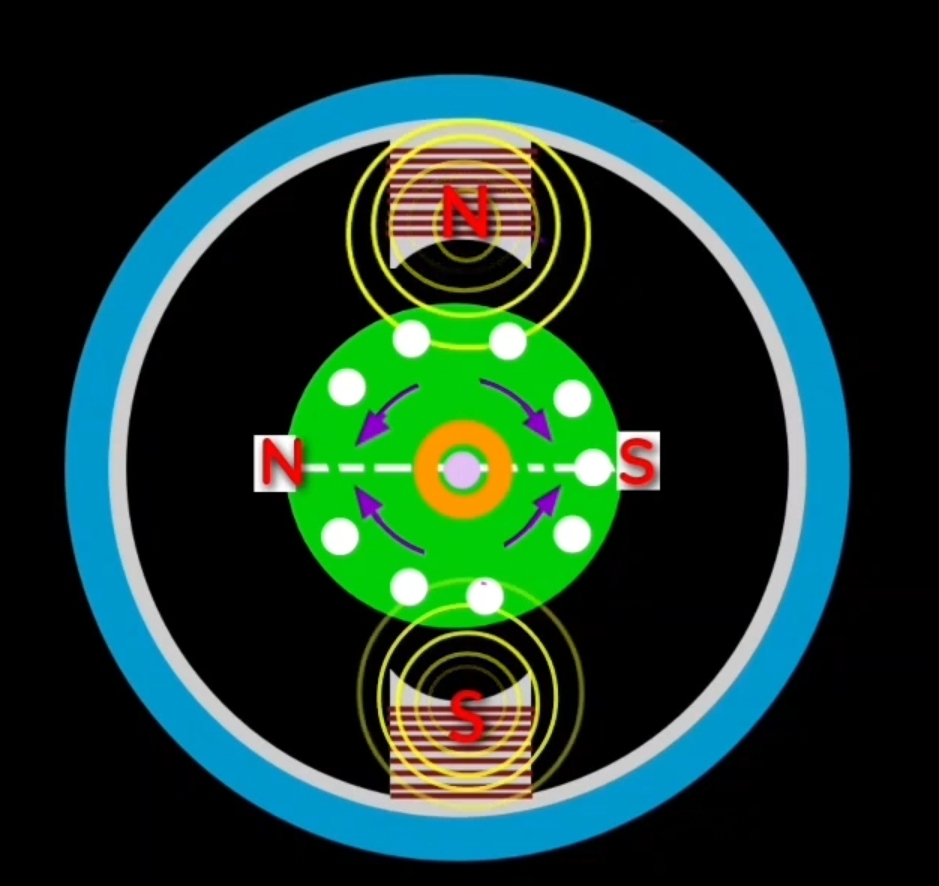
When brush axis perpendicular to the field exis then in this condition also torque will not act on the rotor. Because applied torque on upper and lower conductor is opposite. So in this condition EMF neutralize in rotor conductor, due to zero current in the rotor conductor net torque becomes zero. So in this condition of carbon brush rotor does not rotate in any direction.
Case – 3 : brush axis is in between 0° to 90° angle in clockwise direction from field axis.
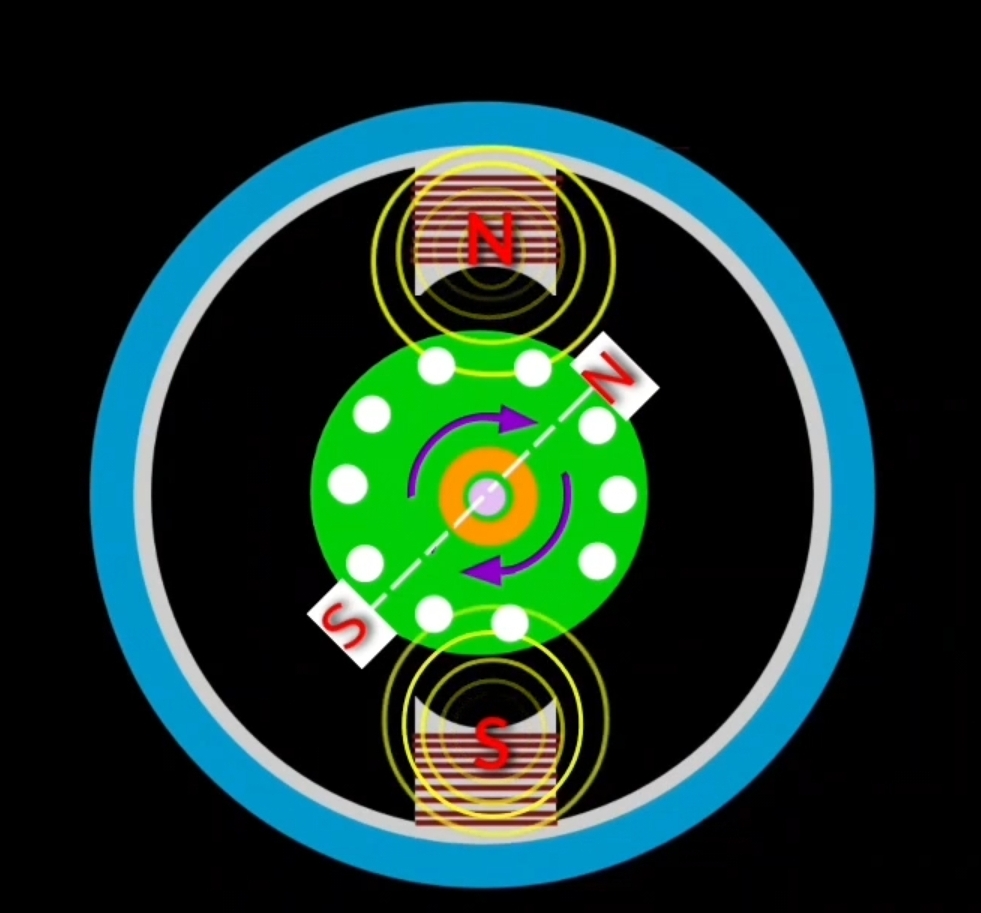
generally brush position is shifted at 45 ° in clockwise direction. In this condition when EMF induces in rotor conductor then N-pole develops on upper right brush and S-pole develops on lower left brush. In this condition repulsion force apply on the rotor between similar magnetic polarity of stator pole and rotar conductor. Stator N-pole repel the rotor N-pole and stator S-pole repel the rotor S-pole.
As a result rotar experience a tour in clockwise direction so rotor starts to rotate in clockwise direction.
and suppose during negative half cycle of a current magnetic polarity on stator and rotor will be change. N-pole will be replace by S-pole and S-pole will replace by N-pole on stator and rotor that you can see in below diagram.

as a result S-pole on stator upper portion will repel rotor S-pole and N-pole on lower portion of stator will repel N-pole of rotor. So rotor will continue rotate in clockwise direction during positive half cycle as well as negative half cycle of AC current.
to rotate the rotor in anticlockwise direction position of brush will change/ shift at 0 to 90° in anti clockwise direction.
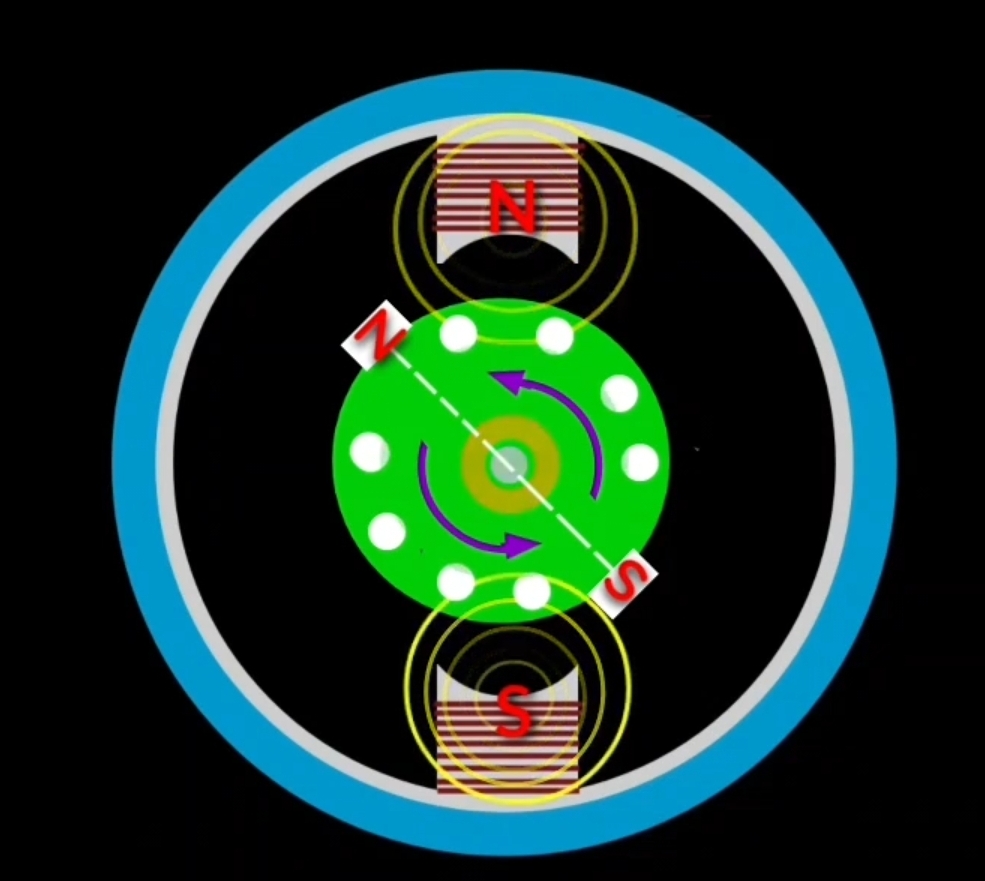
in this condition when torque will act on rotor , rotar will rotate in anticlockwise direction.
Characteristics of repulsion motor
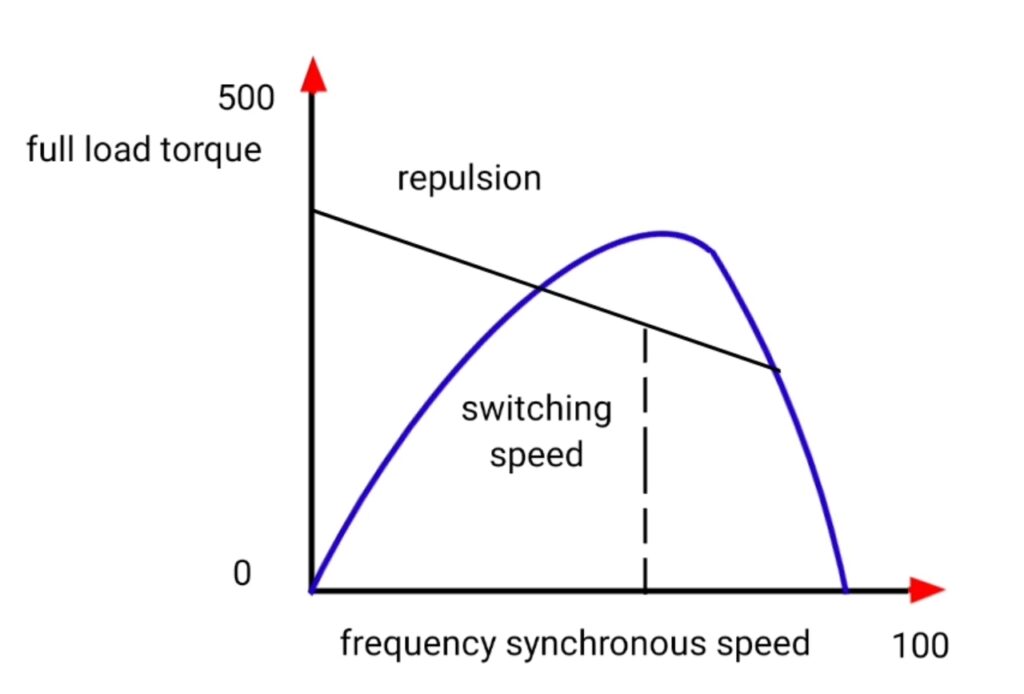
- high starting torque and high speed at no load.
- It has low starting current and high starting torque.
- Speed of the motor for given load depends upon the position of carbon brushes that attached with the rotor of repulsion motor