Tariff is defined as rate at which generated electrical energy provided to the consumers, known as electricity tariff for electrical tariff. Rate of electricity tariff is determined by considering different factors including timing and types of load like industrial load, commercial load and domestic load.
Objective of electricity tariff
Recovery of cost of electrical energy generate at generating station :
to generate the electrical energy at generating station there are different type of machine and equipments are used like large size alternator, three phase transformer, turbines, induction motors, boiler that is used to convert water into steam etc.
so to operate these machines and equipments during generating electricity providers spend money and they receive charge from consumer as electricity bill to recover invested cost during generation of electrical energy. Mean electricity providers recover overall cost to generate electricity from consumers at particular rate according to types of load and timing.
Recovery of cost in Transmission and distribution of electrical energy
to transmit the electrical energy to the consumer we install transmission, lines large size Tower, and large insulators are used to insulate the transmission conductors so this equipments are very expensive so rate of electricity tariff depends on costs of transmission and distribution electrical energy should be recover.
Maintenance cost should be recover
Generated electrical energy transmitted through transmission lines from generating station to receiving station. Some time faults occur in transmission conductor due to different reasons like transient voltage, short circuit fault like line to ground fault, line to line fault, double line to ground fault etc. so maintenance cost during transmission of electrical energy, also recover from consumers by considering particular rate of electricity tariff.
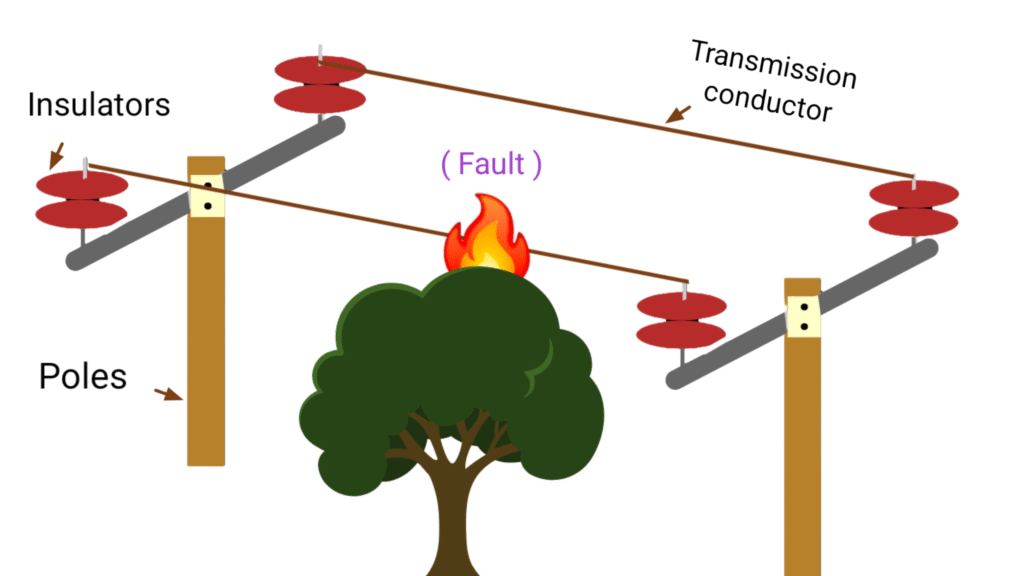
Generating station should not get more profit from consumers
rate of tariff remain always minimum according to the investment for generating electrical energy by the company. It is very important point in objective of electrical energy that electricity provider company decides the rate of tariff according to investment of producing electrical energy, where rate always remain minimum so that company did not get more profit.
Types of electricity tariff
- Simple tariff or uniform electricity tariff : in simple tariff, rate of electricity per unit, remain fixed and consumers, give the charge as per unit rate. Suppose rate of electricity is 3 rs/unit and you are using 20 unit in a month, so you will have to pay 60 rupees in a month.
Main demerit of this type electricity tariff, same charge, apply for the small and big consumers. charges don’t depend upon type of load, it depend upon number of units in case of simple tariff. - Flat rate tariff : inflator rate of electricity tariff is depend upon types of load that is light load or heavy load. When we use the electrical energy for domestic purpose like bulb, fan, television, refrigerator, washing machine etc. then it is known as domestic load or light load. So suppose rate of electricity tariff for light load or domestic load is (60 P/unit).
and when we use heavy machines, like 3 phase induction motor, alternators, dc generator, turbines heavy engines that are known as heavy loads. So for heavy loads, rate of electricity is 55 P/unit.
main demerit of this type tariff, it is expensive for domestic load or light load, While it is less expensive for industrial load or heavy load. - Block rate tariff : in block rate elecyricity tariff, rate of unit is divided into different blocks. Suppose we have four blocks and each blocks have 40 unit. If consumer consumed the 40 unit from first Block within one month, then he will purchase next block in which 40 unit is available. So if consumer will purchase second block within one month, then rate of tariff in second block will be reduce compare to 1st block.
because if rate of tariff for first block is 60P/unit and when we will purchase next block within one month, then rate of second block will be 55P/unit.
and if you will consume two blocks within one month, then you will purchase third block and when you will purchase third block of electricity tariff within one month then rate of third block will be less compare to previous two blocks. To purchase third block, you will pay (55 P/unit) which is less than block one and two. So, it is an advantage of block rate electricity tariff when you will purchase next block within one month, then you will have to pay minimum amount compare to previous block. - Two part tariff : in two part tariff rate is divided into two parts
a) maximum demand – maximum amount of electricity used by consumer is called maximum demand. Suppose any industry have maximum demand is 8 Kv and a particular rate will be fixed for maximum demand suppose 1000 Rs is fixed for 8 kv for that industry. So 1000 will be add with running charge of the company.
b) Running charge – We give the charge as per units, particular rate of unit is decided by the company for running charge. Example 60p/unit .
So in two part tariff total charge will receive from consumers by adding (maximum demand + running charge)
- Maximum demand tariff : it is almost similar as to part tariff but in case of maximum demand tariff a maximum demand meter is installed for measure the maximum demand of the consumers.
- Power factor tariff : in this type of electricity tariff rate depends upon power factor.
Power factor = Cos Ø , it is the cosine angle of voltage and current. - Three part tariff : three part tariff is almost similar to two part tariff but in this tariff semi charge will be add. Mean total charge will be received from consumers by adding (maximum demand tariff + running charge + semi charge ) , semi charge, apply on consumer for recover the maintenance cost of labours and engineers.
so this tariff is called as three part tariff because it divided into three parts, maximum demand, running charge, and semi charge.
