Servo motor is the special purpose machine that converts electrical input into mechanical acceleration with precise angular velocity. Servo Motor is also known as control motor. In this lecture we will learn construction and working principle of Servo motor.
Construction of servo motor
this type of motor is also consists with two important part like other motors that is stator and rotor
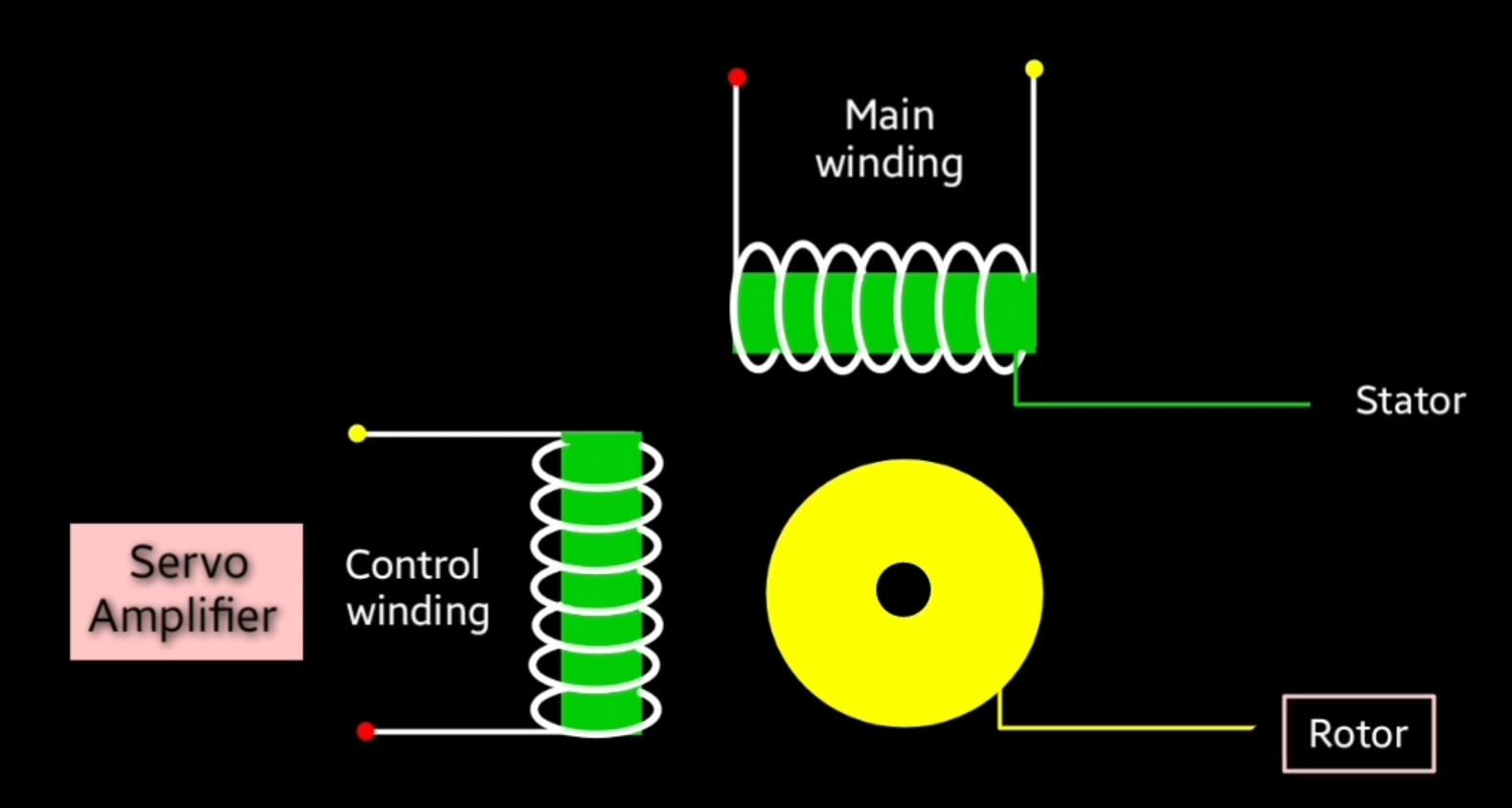
two types of windings are present on stator that is main winding ( fixed winding) and control winding both windings are placed at an angle of 90 degree .
main winding inergize by constant AC voltage signal and control winding energyzed by variable control voltage. To obtain variable control voltage servo motor amplifier is used. When both windings are innergize then phase difference create because both windings are separate at an angle of 90 degree, as a result torque acts on the rotor.
there are two types of rotor are used in the servo motor. Squirrel cage rotor and Drag cup rotor .
Squirrel cage rotor : squirrel cage rotor has large length and it’s diameter is smaller. Aluminium bars are used in squirrel cage rotor to reduce weight of the motor, due to smaller diameter of this type rotor small air gap creates between aluminium bars, it results in reduction of magnetizing current.
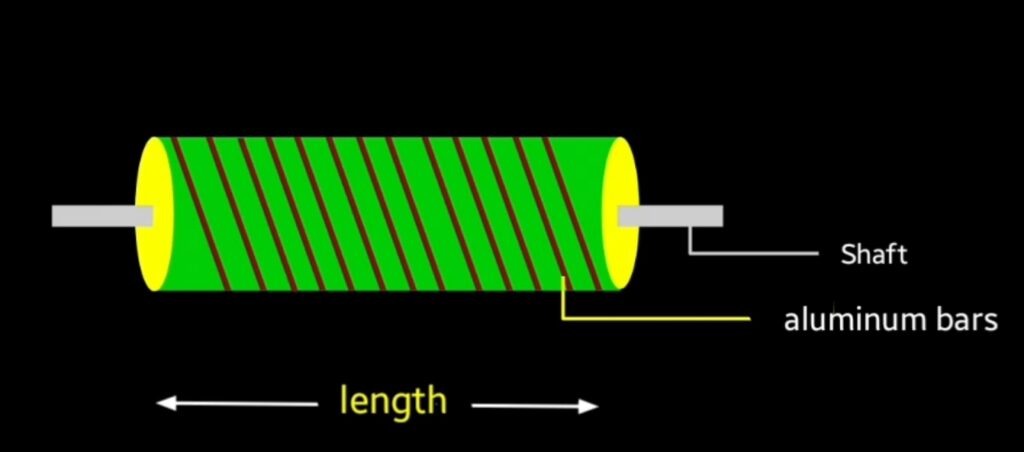
Drag type rotor : it consist of laminated aluminium core where drag Cup is present with some air gap. Drag Cup attached with driving shaft this rotor is used in low power requirement application.
Working principle servo motor
shaft of motor is attached with reduction gearbox which reduces the RPM of motor.
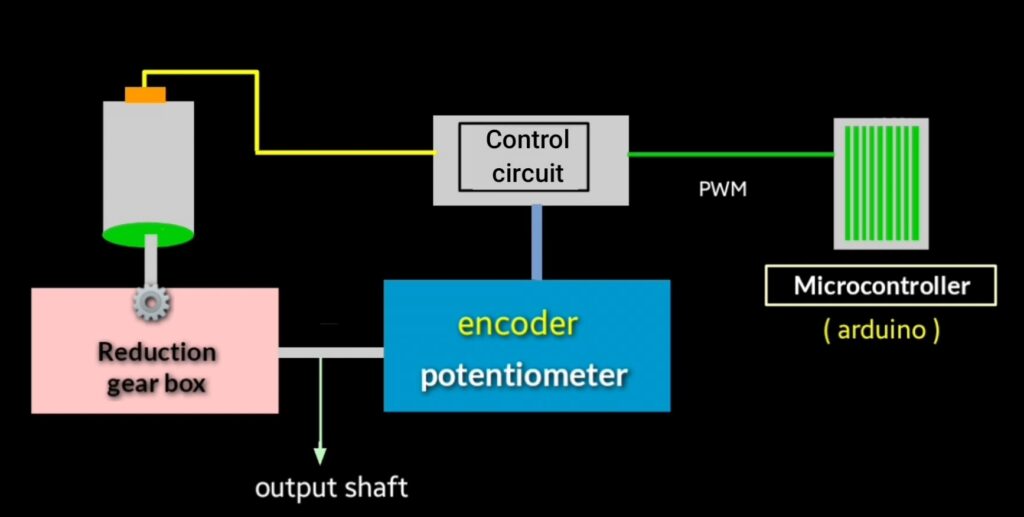
shaft of gearbox is attached with the motor shaft and Potentiometer or encoder is connected with the outputs of gearbox. Output of potentiometer is connected to the control circuit and input wire of the motor is connected to the control circuit. Mean it look like a closed loop system
microcontroller is used to control the servo motor. Microcontroller send signal in the form of PWM to the control circuit. Now control circuit decode the PWM signal that rotor will rotate at how much angle. Control winding of servo Motor is connected to the control circuit so according to input signal received by control circuit motor rotates at particular angle, decides by the control circuit.
and output shaft of gearbox will also rotate with motor shaft and connected encoder send the feedback signal to the control circuit. When control circuit sends the feedback signal that allows to stop the motor at particular angle. And if again microcontroller send the PWM signal to the control circuit then same process will be repeats and rotor will rotates at particular angle that decide by the control circuit.
suppose in this arrangement rotor position is at 20°. and Microcontroller send the PWM signal to the control circuit for rotate the rotor at 60° angle. As well as control circuit get feedback signal from encoder, control circuit stops the rotor at 60°.
Torque speed characteristics of servo motor.
Servo motor is designed to provide linear Torque speed characteristics
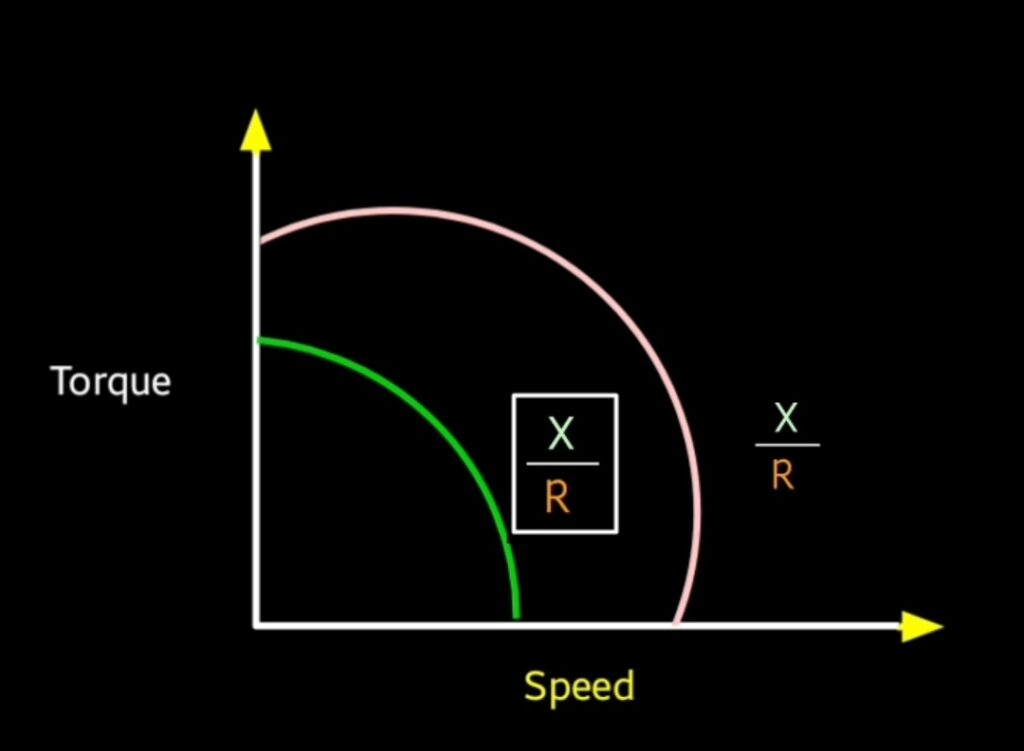
but actually when we go through in the above diagram graph is not linear because it depends upon the reactance to resistance ratio. If reactance to resistance ratio is minimum then graph will be more linear.
Speed control
Generally 3 methods are used to control the speed of AC Servo Motor
- position control method
- torque control method
- speed control method
Position control : the position control method is used to determine the size of the rotating speed through external input frequency. And the angle of revolution is determined by the number of pulse.
Torque control method : in the torque control method the output torque of the servo motor is set by analogue input at the address. And it can change the torque simply by changing the analogue real time.
Speed control : in a speed control method motor speed can be controlled by analogue Input and pulse.